RAM memory: types, differences and what is the amount you need to have on your PC or mobile
amount of RAM memory for a computer, mobile, or any other device is vital to obtain the performance we are looking for, and not to
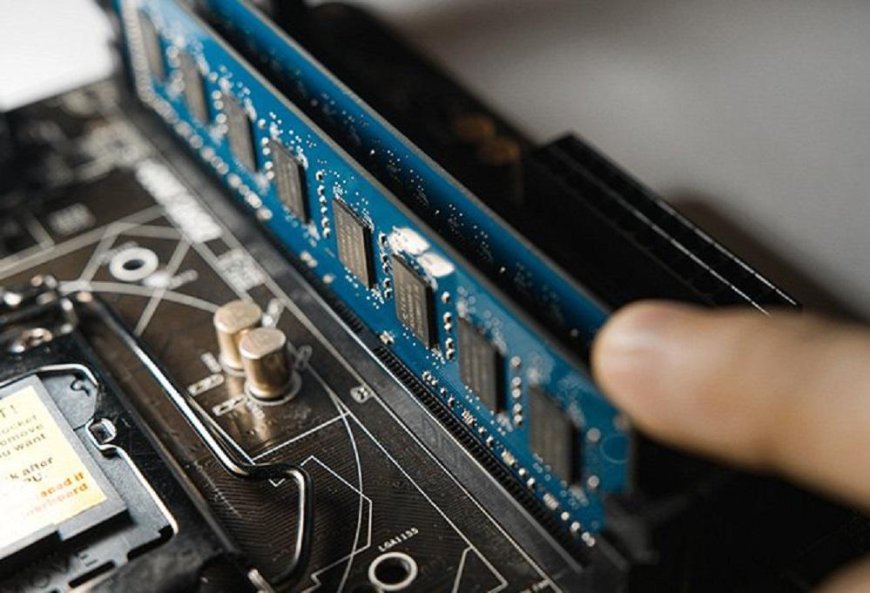
Correctly choosing the type and amount of RAM memory for a computer, mobile, or any other device is vital to obtain the performance we are looking for, and not to waste money.
In the technological devices that we use today, there are three or four hardware components that provide 80% of the performance: the processor or CPU, the graphics chip or GPU, and the RAM.
Of course, there are quite a few more, from the type of storage memory, to the data bus and motherboard baud rates.
But most of the raw performance is guaranteed by the three mentioned: CPU, GPU and RAM. Among them, RAM is possibly the least known, and the most underrated.
Let's see what RAM is: types, differences and how much you need to have on your smartphone and PC.
We will focus on the memories that are used today, and how to correctly choose the type and quantity, depending on our needs.
All about RAM for PC and mobile
- What is RAM
- For what do you use it?
- RAM types
- SDRAM connection types
- DDR memory
- Speed
- Latency
- Latency / Speed ‹‹vs. Amount of memory
- ECC, XMP profile and other terms
- Double or quad channel
- How to choose memory on a PC
- How much RAM do I need in a PC?
- RAM memory in mobiles
- How to choose memory in mobiles
- How much RAM do I need in a mobile?
What is RAM
The memory of a device is a chip, or a group of chips, where data is stored.
There are many types of memory: RAM, ROM, hard drives, SSD, Flash memory, and many more. In some, data is stored permanently (it is recorded once and cannot be erased), such as ROM. In others they are kept for years, until we erase them, such as a hard drive.
One of the most used is RAM (Random Access Memory), Random Access Memory.
Its main characteristic is that it is a volatile memory, that is, it only stores data temporarily, while the device is turned on and the memory has current.
When you turn it off, the data is erased and the RAM is emptied.
It is called Random Access Memory because it is possible to access any data contained in memory at the same speed, no matter where it is.
It is much more efficient than other memories such as hard drives, where you have to move a head across the entire disk, and reaching some areas takes longer than others.
For what do you use it?
RAM is a very fast memory, but it is also considerably more expensive than a hard disk, or an SSD, for example.
Its main function is to store the data that the processor or CPU is handling at all times.
Must Read: The Sony Xperia Pro 1 would arrive with a camera with a 1-inch sensor
Normally the CPU extracts the data from the hard disk or Flash memory, places it in RAM, processes it, and sends the result back to the hard disk, or to video memory (the graphics chip has its own memory ), or to a peripheral that requires it, such as a printer.
Understanding what it does, it is easy to see that the more RAM we have and the faster it is, the better performance we will get from the device.
RAM types
Within these volatile and random memories, there are many different types: SRAM, NVRAM, MRAM, RDRAM, etc.
It is not the intention of this article to explain all of them, but to focus on those that are used as main memory in mobiles and computers. That is the memory SDRAM, or Synchronous Dynamic RAM, memory of dynamic and synchronous access.
It is synchronous because it synchronizes with the motherboard data bus to improve performance. And it is dynamic because the processor can allocate different amounts of memory to apps or processes, as needed.
SDRAM connection types
SDRAM memory is connected in different ways depending on whether it is a desktop PC, a laptop, or a mobile device.
Let's see the different types that exist.
DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module)
It is an elongated memory that is inserted into the motherboard of a tower or desktop PC.
The notch is not in the center, so it only fits the plate in the correct direction.
SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM)
It is the memory that many laptops use.
It is similar to the DIMM but shorter, with less capacity and somewhat slower.
Memory soldered to the board
Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, and some laptops, use RAM that is soldered to the board.
This eliminates parts and allows it not to move, but has an obvious disadvantage: it cannot be expanded or exchanged for a faster one, or with more capacity.
DDR memory
To recap, we have seen that modern devices use SDRAM memory, with different connection types.
In addition, within the SDRAM memory there are different types, depending on their technology and performance.
Modern SDRAM memory is of the DDR type, or Double Data Rate. It is characterized in that the memory can transmit data through two different channels at the same time, in a single clock cycle. With this system the performance is doubled.
It is not something new, since they began to be used almost 20 years ago, that is why DDR-SDRAM memory has evolved: DDR, DDR2, DDR3, etc.
The speed of the RAM memory is measured in Megahertz per second (MT / sg), although commercially Megahertz or MHz are often used.
DDR: It reached a speed of 266 MT / sg, and a consumption of 2.5V. 184 pin connector
DDR2: Speed ‹‹of 400 MT / sg, and a consumption of 1.8V. 240-pin DIMM connector
DDR3: Speed ‹‹of 1,066 MT / sg, and a consumption of 1.5V. 240-pin DIMM connector
DDR4: Speed ‹‹of 3,200 MT / sg, and a consumption of 1.2V. 288-pin DIMM connector
DDR5: Speed ‹‹of 5,200 MT / sg, and a consumption of 1.1V. 288-pin DIMM connector
As we can see, the higher DDR the memory is faster and the consumption is lower, so it heats up less.
Currently the one that is most used, both in mobile phones and PCs, is DDR4 memory. The above are considered outdated, but are still sold for old computers.
Some PCs and mobiles with DDR5 have already started to be seen, but it is still very rare.
Some brands instead of DDR2, DDR3, etc, call it PC2 or PC3, but they refer to the same thing.
Speed
Within the same type of memory DDR3, DDR4, etc., there are different speeds.
We have seen how memory speed is measured in Megahertz per second (MT / s), but in practice in store catalogs Megahertz (MHz) is used.
Thus, for example, we can find DDR4 RAM modules at 2,400, 2,600, 3,000, 3,200, up to 3,600 Mhz.
Obviously the faster the RAM the better, but it is also more expensive. And, an important fact, the motherboard of your PC must support that speed. If it only accepts 2,400 Mhz and you put a 3,200 Mhz memory, it will work at 2,400 Mhz.
Since almost all computers use multiple memory modules, it is recommended that they all operate at the same speed. You can mix speeds, but they will all run at the speed of the slowest module. If you put 3 RAM modules at 3,600 Mhz and 1 at 2,400 Mhz, all 4 will work at 2,400 Mhz.
Latency
Another very important data of the RAM memory of the PC, is the latency.
RAM memory modules have numbers associated with them, called timings. For example, 9-8-9-17. This data indicates the performance of these particular chips, measured in nanoseconds.
The most important value is the first, called the CAS or CL latency. The CL measures the number of clock cycles it takes for RAM to deliver data to the memory controller, when required. The lower the CL, the better.
Within the DDR4 memory and within the same speed, for example 3,600 Mhz, you will see that modules are sold with CL 16 or CL 18, for example.
The lower the value, the faster the memory, but also the more expensive.
Note that you cannot compare between different generations of DDR. For example, DDR3 memory has lower CLs than DDR4, which is better in theory, but it is much slower in other sections, so DDR4 continues to offer much better performance.
Latency / Speed ‹‹vs. Amount of memory
Many users, when they buy RAM, only look at it being DDR4, and choose as much as possible.
But don't underestimate speed and latency, especially if you play video games. You may be more interested in mounting 16 GB at 3,600 Mhz with CL16, than 32 GB at 2,400 Mhz with CL18.
For office or video applications, it may be more important to have more RAM, speed and latency take a backseat.
ECC, XMP profile and other terms
We are going to explain other loose terms that are also in common use when working with RAM.
ECC or Error Correcting Code is a type of SDRAM memory capable of detecting errors in data transmission, and correcting them. It is only used on professional computers and servers.
The XMP or DOCP profile refers to data associated with each RAM memory model. The profile is activated in the BIOS, and allows you to configure it to the correct speed.
If you install new memory in your PC, it will probably run much slower than its actual speed. You must enter the BIOS, look for the XMP or DOCP profile option, and activate it, to correctly configure the RAM and make it work at maximum speed.
Double or quad channel
Finally, you have to know that motherboards accept dual or quad channel memories. In other words, you should always install 2 or 4 memory modules, not 1 or 3.
If you are going to install 32 GB of RAM, do not put 1 32 GB module. Put 2 of 16GB in the slots indicated by the motherboard manual. It can even give more performance to put 4 modules of 8 GB.
How to choose memory on a PC
To expand the RAM memory of your PC or mount a new one from scratch, look for your motherboard manual and check how many free memory connectors you have, the type of DDR, the maximum amount of memory allowed, and its speed.
With this data, buy DDR 3 or 4 memory at the maximum speed of your motherboard, and with the lowest possible latency (CL).
Always install even modules in the slots indicated in the motherboard manual, since if you have 4 connectors and you buy 2 RAM memory modules, they are not normally inserted in connectors 1 and 2, but in connectors 1 and 3.
How much RAM do I need in a PC?
The big question for many, but it is easy to get the idea.
These are our RAM memory recommendations for a PC in 2021:
- 4 GB: basic PC for office automation
- 8 GB: standard PC or leisure (watch Netflix, social networks, etc).
- 16 GB: PC gaming or video editing
- 32GB: PC gaming with AAA games, streaming while you game, 4K video editing
RAM memory in mobiles
The memory of mobiles is similar to that of PCs, but smaller, slower, and soldered to the motherboard, so it cannot be expanded or improved.
They also use DDR SDRAM memory, but it is called LPDDR or Low Power DDR (low power DDR), because it consumes less.
As in PC, the most common is LPDDR4, although there are extensions, LPDDR4X, and there are already a few high-end mobiles that use LPDDR5, such as the Samsung Galaxy S21
We hope we have helped you, surely now you have everything clearer.
